Discover the Women of the Hall
These are the Inductees of the National Women’s Hall of Fame. Select any of the women to discover their stories and learn how they have influenced other women and this country.

St. Frances Xavier Cabrini
Established orphanages, day care centers, schools, clinics and hospitals for immigrants in the United States and around the world. She established a missionary order of women and was the first American citizen to be canonized a saint.

Mary Steichen Calderone
Pioneering sex educator and acknowledged “mother of sex education.” She established the Sex Information and Education Council of the United States, which established sexuality as a healthy entity. Dr. Calderone was President of the SIECUS board, as well as author and co-author of several books, professional journals and magazine articles.

Annie Jump Cannon
Astronomer who perfected the universal system of stellar classification. While working at Harvard Observatory, Cannon compiled the largest accumulation of astronomical information ever assembled by an individual.

Rachel Carson
Zoologist whose concern over the damaging effects of pesticides and other poisons on the environment led to her groundbreaking work, Silent Spring. Carson’s book was a catalyst for the environmental movement of today.

Eleanor Rosalynn Smith Carter
Former First Lady (1977-1981), Rosalynn Carter was an advocate for mental health, early childhood immunizations, human rights, conflict resolution, and health promotion worldwide.

Mary Ann Shadd Cary
An educator and abolitionist, Mary Ann Shadd Cary was the first Black American woman to enroll in and graduate from Howard University Law School. She appeared before the House Judiciary Committee to argue for the right of women to vote (with Anthony and Stanton). During the 1870s, while practicing law, she lectured throughout the United States about the improvement of education for Black Americans.

St. Frances Xavier Cabrini
Established orphanages, day care centers, schools, clinics and hospitals for immigrants in the United States and around the world. She established a missionary order of women and was the first American citizen to be canonized a saint.

Mary Steichen Calderone
Pioneering sex educator and acknowledged “mother of sex education.” She established the Sex Information and Education Council of the United States, which established sexuality as a healthy entity. Dr. Calderone was President of the SIECUS board, as well as author and co-author of several books, professional journals and magazine articles.

Annie Jump Cannon
Astronomer who perfected the universal system of stellar classification. While working at Harvard Observatory, Cannon compiled the largest accumulation of astronomical information ever assembled by an individual.

Rachel Carson
Zoologist whose concern over the damaging effects of pesticides and other poisons on the environment led to her groundbreaking work, Silent Spring. Carson’s book was a catalyst for the environmental movement of today.

Eleanor Rosalynn Smith Carter
Former First Lady (1977-1981), Rosalynn Carter was an advocate for mental health, early childhood immunizations, human rights, conflict resolution, and health promotion worldwide.

Mary Ann Shadd Cary
An educator and abolitionist, Mary Ann Shadd Cary was the first Black American woman to enroll in and graduate from Howard University Law School. She appeared before the House Judiciary Committee to argue for the right of women to vote (with Anthony and Stanton). During the 1870s, while practicing law, she lectured throughout the United States about the improvement of education for Black Americans.

Mary Cassatt
American impressionist painter who captured the soul of family life, women, children, interiors and gardens. A friend and student of the great Impressionists of Paris, Cassatt powerfully influenced American art.

Willa Cather
Newspaperwoman and editor who became an outstanding novelist with the publication of O Pioneers in 1913. Cather went on to write other great novels and won the Pulitzer Prize in 1922. Her well-known works include My Antonia and Death Comes for the Archbishop.

Carrie Chapman Catt
Tenacious women’s suffrage organizer whose efforts at the helm of the National American Women Suffrage Association put forth the “winning plan” that led to state-by-state enactments of suffrage and the final victory in 1920.
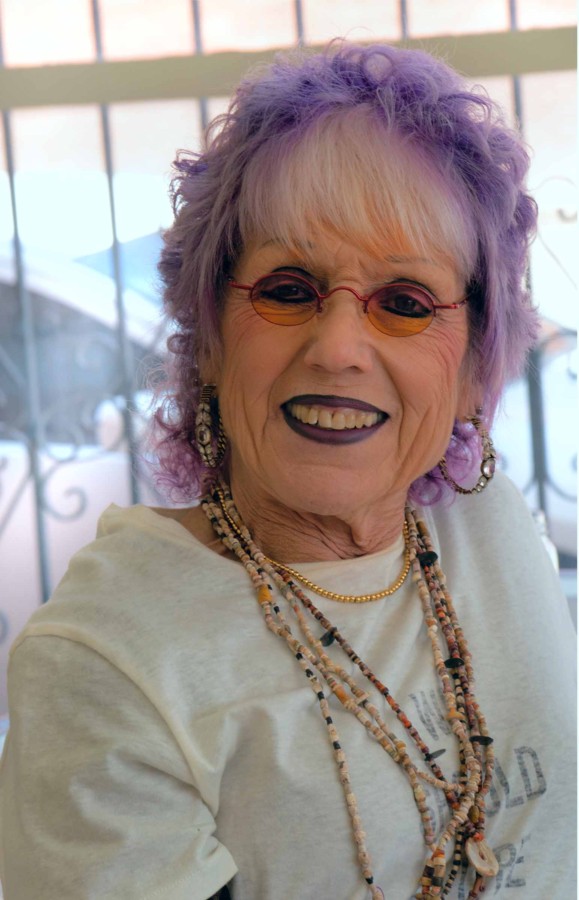

Judy Chicago

Julia Child
A graduate of Smith College, Julia Child went on to attend classes at Le Cordon Bleu in Paris. The famous American cook, author, and television personality introduced French cuisine and cooking techniques to America through her cookbooks and television programs. Her most famous works include the 1961 cookbook Mastering the Art of French Cooking and the television series The French Chef, which premiered in 1963. She is widely credited with demystifying the art of fine cooking.

Lydia Maria Child
Author and social reformer, Lydia Maria Child spent a lifetime crusading for the abolition of slavery and supporting women’s suffrage. As the author of more than 40 books and the editor of eleven publications, she was always addressing the main issues of 19th century America.

Mary Cassatt
American impressionist painter who captured the soul of family life, women, children, interiors and gardens. A friend and student of the great Impressionists of Paris, Cassatt powerfully influenced American art.

Willa Cather
Newspaperwoman and editor who became an outstanding novelist with the publication of O Pioneers in 1913. Cather went on to write other great novels and won the Pulitzer Prize in 1922. Her well-known works include My Antonia and Death Comes for the Archbishop.

Carrie Chapman Catt
Tenacious women’s suffrage organizer whose efforts at the helm of the National American Women Suffrage Association put forth the “winning plan” that led to state-by-state enactments of suffrage and the final victory in 1920.

Judy Chicago

Julia Child
A graduate of Smith College, Julia Child went on to attend classes at Le Cordon Bleu in Paris. The famous American cook, author, and television personality introduced French cuisine and cooking techniques to America through her cookbooks and television programs. Her most famous works include the 1961 cookbook Mastering the Art of French Cooking and the television series The French Chef, which premiered in 1963. She is widely credited with demystifying the art of fine cooking.

Lydia Maria Child
Author and social reformer, Lydia Maria Child spent a lifetime crusading for the abolition of slavery and supporting women’s suffrage. As the author of more than 40 books and the editor of eleven publications, she was always addressing the main issues of 19th century America.

Shirley Chisholm
First African American woman elected to the U.S. Congress. Chisholm was also the first African American woman to receive delegate votes for the presidential nomination of a major party. A member of Congress for many years, she was also an educator and writer.

Hillary Rodham Clinton
Hillary Rodham Clinton is the first First Lady ever to be elected to the United States Senate. She is the first woman Senator from New York. Her efforts on behalf of women’s, family and children’s issues began during her earliest employment as an attorney and remain steadfast today. Senator Clinton is the first New York State Senator to serve on the Senate Armed Services Committee.

Elouise Cobell
Known as “Yellow Bird Woman,” Elouise Cobell was an entrepreneur, banker, advocate, and member of the Blackfeet Nation who fought tirelessly for government accountability and for Native Americans to have control over their own financial future.

Elizabeth Jane Cochran
Trail-blazing journalist considered to be the “best reporter in America” who pioneered investigative journalism.

Jacqueline Cochran
First woman aviator to break the sound barrier. A leader and pilot, Cochran held many speed, distance and altitude records. She led the Women’s Air Force Service Pilots during World War II, becoming the first woman to pilot a bomber across the Atlantic Ocean.

Mildred Cohn
A groundbreaking scientist in several important areas of biological research, Mildred Cohn pioneered research that helped form the scientific understanding of mechanisms of enzymatic reactions and the methods of studying them. In 1946, she introduced the use of isotopic oxygen 18 to study metabolic processes and enzyme mechanisms. She later applied nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) to investigate metabolism and metabolic intermediates. Cohn has published more than 150 scientific papers and has received several awards for her work, including the National Medal of Science in 1982.

Shirley Chisholm
First African American woman elected to the U.S. Congress. Chisholm was also the first African American woman to receive delegate votes for the presidential nomination of a major party. A member of Congress for many years, she was also an educator and writer.

Hillary Rodham Clinton
Hillary Rodham Clinton is the first First Lady ever to be elected to the United States Senate. She is the first woman Senator from New York. Her efforts on behalf of women’s, family and children’s issues began during her earliest employment as an attorney and remain steadfast today. Senator Clinton is the first New York State Senator to serve on the Senate Armed Services Committee.

Elouise Cobell
Known as “Yellow Bird Woman,” Elouise Cobell was an entrepreneur, banker, advocate, and member of the Blackfeet Nation who fought tirelessly for government accountability and for Native Americans to have control over their own financial future.

Elizabeth Jane Cochran
Trail-blazing journalist considered to be the “best reporter in America” who pioneered investigative journalism.

Jacqueline Cochran
First woman aviator to break the sound barrier. A leader and pilot, Cochran held many speed, distance and altitude records. She led the Women’s Air Force Service Pilots during World War II, becoming the first woman to pilot a bomber across the Atlantic Ocean.

Mildred Cohn
A groundbreaking scientist in several important areas of biological research, Mildred Cohn pioneered research that helped form the scientific understanding of mechanisms of enzymatic reactions and the methods of studying them. In 1946, she introduced the use of isotopic oxygen 18 to study metabolic processes and enzyme mechanisms. She later applied nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) to investigate metabolism and metabolic intermediates. Cohn has published more than 150 scientific papers and has received several awards for her work, including the National Medal of Science in 1982.

Bessie Coleman
The first licensed black female aviator. She earned her international pilot’s license in 1921 and gained fame during the next five years for her air acrobatics and highflying stunts. She dreamed of starting a school to train black aviators.

Eileen Collins
First American woman to pilot a spacecraft. A math teacher at the Air Force Academy and test pilot, Collins served as pilot of the space shuttle Discovery during a mission to rendezvous with space station Mir. In July, 1999 she became NASA’s first female commander in space.

Ruth Colvin
Founder of the Literacy Volunteers of America, a group which she began in her upstate New York home. The organization has now taught nearly half a million people to read. Its unique approach, designed by Colvin, employs community tutors.

Rita Rossi Colwell
Dr. Rita R. Colwell became the first woman and first biologist to head the National Science Foundation in 1998, spearheading the agency’s emphases in K-12 science and mathematics education, graduate science and engineering education/training and the increased participation of women and minorities in science and engineering.

Joan Ganz Cooney
Founder of the Children’s Television Workshop for Public Television and creator of Sesame Street. Cooney created a study for the Carnegie Corporation on the possible use of television for preschool education. Acting on her own findings, she solicited funds to develop a program for television. For this, she was the winner of the Emmy and Peabody Awards, along with other honors.
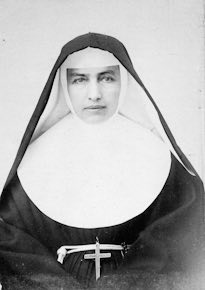
Mother Marianne Cope
As a Sister of the Third Order of St. Francis, Mother Marianne Cope worked for several years in Syracuse, New York, helping to found St. Joseph’s Hospital. In 1883, she went to Kalaupapa, Hawaii where she spent thirty years ministering to those with leprosy. While in Hawaii, she worked hand in hand with Father Damien during the last part of his life.

Bessie Coleman
The first licensed black female aviator. She earned her international pilot’s license in 1921 and gained fame during the next five years for her air acrobatics and highflying stunts. She dreamed of starting a school to train black aviators.

Eileen Collins
First American woman to pilot a spacecraft. A math teacher at the Air Force Academy and test pilot, Collins served as pilot of the space shuttle Discovery during a mission to rendezvous with space station Mir. In July, 1999 she became NASA’s first female commander in space.

Ruth Colvin
Founder of the Literacy Volunteers of America, a group which she began in her upstate New York home. The organization has now taught nearly half a million people to read. Its unique approach, designed by Colvin, employs community tutors.

Rita Rossi Colwell
Dr. Rita R. Colwell became the first woman and first biologist to head the National Science Foundation in 1998, spearheading the agency’s emphases in K-12 science and mathematics education, graduate science and engineering education/training and the increased participation of women and minorities in science and engineering.

Joan Ganz Cooney
Founder of the Children’s Television Workshop for Public Television and creator of Sesame Street. Cooney created a study for the Carnegie Corporation on the possible use of television for preschool education. Acting on her own findings, she solicited funds to develop a program for television. For this, she was the winner of the Emmy and Peabody Awards, along with other honors.

Mother Marianne Cope
As a Sister of the Third Order of St. Francis, Mother Marianne Cope worked for several years in Syracuse, New York, helping to found St. Joseph’s Hospital. In 1883, she went to Kalaupapa, Hawaii where she spent thirty years ministering to those with leprosy. While in Hawaii, she worked hand in hand with Father Damien during the last part of his life.
